Imagine a future where people who have lost their ability to speak can communicate again—just by thinking. This is no longer science fiction. Thanks to breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI), scientists are now able to decode thoughts into words using non-invasive brain scans.
Musumeci Online – The Podcast. It is perfect for driving, commuting, or waiting in line!
In simple terms, AI is learning to understand the language of our brains, opening up incredible possibilities for medicine, neuroscience, and human communication.
The Power of AI to Read the Brain
For years, researchers have been trying to understand how the brain processes language. We know that when we speak, read, or even think of words, our brain activity follows certain patterns. The challenge has always been translating these patterns into actual sentences. Until now, this required invasive brain implants, making the technology impractical for most people.
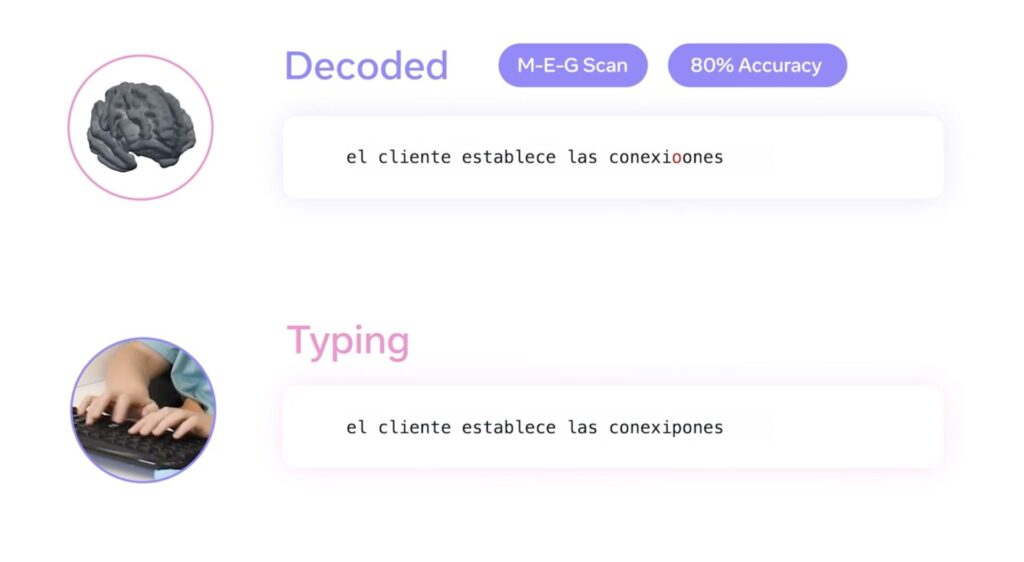
A team of scientists from Meta’s Fundamental AI Research (FAIR) lab, in collaboration with the Basque Center on Cognition, Brain and Language in Spain, has made a major leap forward. By using AI to analyze non-invasive brain scans, they have been able to decode up to 80% of characters in a sentence—often enough to reconstruct entire phrases. This means that for the first time, we can turn brain activity into readable text without surgery.
How Does It Work?
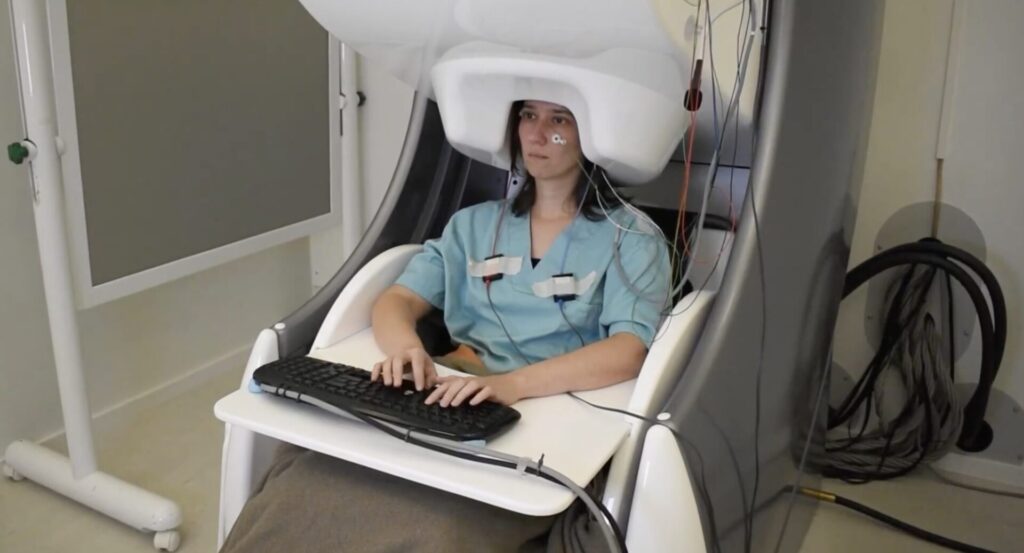
To achieve this breakthrough, researchers used two types of brain-scanning technology:
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG): Captures tiny magnetic fields generated by neurons.
- Electroencephalography (EEG): Measures the brain’s electrical activity.
Participants in the study were asked to type sentences while their brain activity was recorded. The AI was then trained to recognize the patterns associated with different letters and words. When tested with new sentences, the AI successfully predicted up to 80% of the characters using MEG—twice as accurate as previous EEG-based models.
A Game-Changer for People Who Can’t Speak
Why is this important? Millions of people worldwide suffer from brain injuries or conditions like ALS, which rob them of their ability to speak. Currently, communication devices rely on eye movements or muscle control, which can be slow and frustrating. A non-invasive AI-powered brain decoder could give them a faster and more natural way to express themselves—simply by thinking.
Of course, there are still challenges. MEG requires a special magnetically shielded room, and the AI isn’t yet perfect. But this is just the beginning. With further advancements, we could see wearable brain-reading devices that help people communicate effortlessly.
Cracking the Code of Language in the Brain
Beyond helping people regain speech, this research also sheds light on how our brains form language. Scientists have long struggled to study this process because speaking distorts traditional brain scans. However, AI has now helped reveal a fascinating insight: the brain builds language in a step-by-step process, moving from abstract ideas to specific words, syllables, and even individual letters.
AI is not just about robots or chatbots—it’s actively shaping the future of medicine
Think of it like writing a book. First, you outline the main idea (the concept you want to express). Then, you break it down into chapters (phrases), sentences, and finally, individual words. The brain follows a similar sequence when forming speech.
AI and the Future of Health Tech
This breakthrough is part of a bigger trend: using AI to solve complex health challenges. Meta has already partnered with medical researchers to develop AI tools that improve diagnosis and treatment. For example:
- BrightHeart, a French startup, uses Meta’s AI to help doctors detect congenital heart defects in unborn babies.
- Virgo, a U.S.-based company, leverages AI to analyze endoscopy videos, helping doctors diagnose digestive diseases faster and more accurately.
These examples show how AI is not just about robots or chatbots—it’s actively shaping the future of medicine, making life-saving technology more accessible and effective.
The Road Ahead
As AI continues to advance, the potential applications are endless. Imagine a future where AI-powered brain interfaces help stroke survivors regain their speech, or where we can translate thoughts into words in real-time. While there’s still a long way to go, the progress we’re seeing today is bringing us closer to that reality.
One thing is certain: AI is no longer just a tool—it’s a bridge between science and human potential, unlocking new ways to heal, communicate, and understand the world around us.


Leave a Reply